Protocols in simple words are the rules used for
communicating or passing of information between two computers or such devices. Communication
systems need to use a properly defined format when passing messages hence
protocols come in place to solve this problem.
A network consists of several layers and the basic
layers are Application Layer, Transport Layer, Network Layer and other lower
layers. A protocol can be implemented in any of these layers; it could be implemented
in hardware level, software level or both. Protocols are generally defined
using an industry or international standard.
Application layer is the layer that is closest to the
end user. It is a layer, which provides service to ensure effective
communication with other programs in the network is possible. Listed below are
few examples of internationally accepted protocols implemented on the
application layer.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
HTTP is the protocol used by the World Wide Web
(WWW). It defines how messages are transmitted over the web and what actions
the browser should take with regard to commands given. When a URL is entered to
the browser, what actually happens is it sends an HTTP command to the web
server commanding to fetch a requested web page.
It provides a standardized way for computers to
communicate with each other. HTTP specification specifies how clients request
data will be constructed and sent to the serve, and how servers respond to
these requests.
HTTP is said to be a stateless protocol as each command
execution is independent of each other without any knowledge of what command
came in before, making it difficult to build intelligent websites responsive for
user inputs.
HTTP has three basic features, which makes HTTP
simple yet powerful
Connection-less
When HTTP
client makes a request, the client will disconnect and wait for the server to
response. The server will re-establish the connection and send a response back.
Therefore, HTTP is said to be a connection-less protocol.
Media Independent
Via HTTP
protocol client and server can pass data of any type as long as both client and
server knows how to handle the data. When sending a message client and server have
to specify the content type using an appropriate MIME-type.
Stateless
As a result of HTTP
being connection-less the server and client are aware of each other only during
the current session. After the session is finished both return back to their
own work and forget about the other party as a result they cannot retain
information between different requests across the web pages.
HTTP Secure (HTTPS)
HTTPS is a secure communication protocol over a
computer network. HTTPS is not a new protocol. It is the result of layering
HTTP on top of SSL/TLS. A protocol that adds the security capabilities in
SSL/TLS to HTTP protocol.
HTTPS is a mechanism that provides special form of
authentication adopted to avoid man-in-the-middle attack. It provides a special
form of bidirectional encryption to provide security for data flow between
client and server this encryption protect the communication against
eavesdropping and tampering.
Man-in-the-middle attack refers to the ability of another
computer program to alter messages in a communication channel. The said
computer program will place it self between the client and server and monitor
the message passing and alter or inject messages to the communication channel. By using HTTPS uses a special form of encryption
through which only the client and server can decrypt the messages.
Since the Hacker gets only part of the password for
decrypting the message, the hacker is unable to access the content of the
message and interrupt the communication. The encryption process is a wide
subject area; the following diagram gives a basic overall idea about this
process.
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
SMTP is the internet standard for electronic mail
transfer. SMTP is generally used to send messages from a mail client to a mail
server. SMTP generally uses TCP port 25 for its operations. Like HTTP Secured
SMTP secured connection which is build on top of SSL is known as SMTPS.
Electronic mail servers generally uses SMTP for
sending and receiving mail messages, but user-level client applications use
SMTP only for sending messages to a mail server for receiving messages either
POP or IMAP protocols are used.
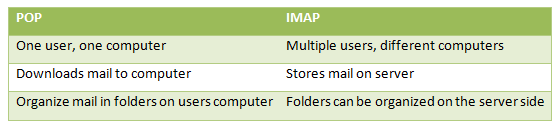
Post Office Protocol/Internet Message Access Protocol (POP/IMAP)
POP & IMAP are application layer protocols used
by local e-mail clients to receive e-mails from a remote server over a TCP/IP
connection.
POP has several versions and the current version in
use is POP3. May webmail service providers such as Gmail, outlook & yahoo
mail provides support for either IMAP or POP3 to allow mail to be downloaded.
IMAP, unlike POP allows multiple clients to
simultaneously connect to the same mailbox and through flags stored on the
server different clients accessing the same mailbox at the same or different
times can detect state changes made by other clients.
File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
FTP is a network protocol used to transfer computer
files from one host to another over a TCP based network. FTP works in a similar
manner to HTTP when transmitting web pages from a server to a user’s browser
and works similar to SMTP when transferring mails across the internet.
The most common use of FTP is to download a file from
a server using the internet or to upload a file to a server.